AI Visualization Tool Provides Power Grid Operators with Data Monitoring and Analysis
A new visualization tool with an artificial intelligence (AI ) component allows power grid operators to make quicker and more informed monitoring and analysis decisions.
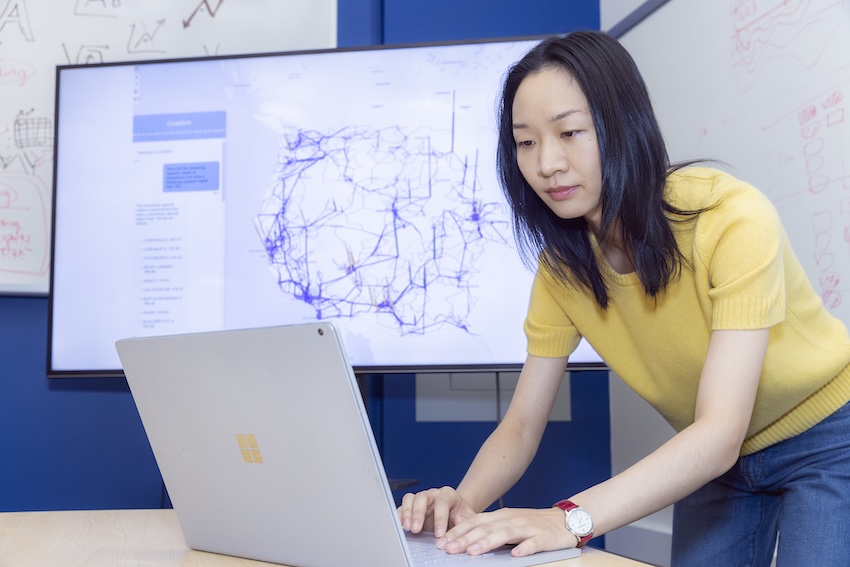
Sichen Jin, a Ph.D. student in the School of Interactive Computing, led the development of ChatGrid while interning at Pacific Northwest National Laboratory PNNL. ChatGrid is a large-scale visual analytic tool with a natural language query-based interface empowered by large-language models (LLMs).
Power grid data monitoring and analysis are critical to ensure reliable and efficient electrical systems operation. However, massive and complex datasets present a challenge. The analysis process typically requires coding for data and visualization generation, which can be time-consuming for grid operators.
ChatGrid alleviates this burden and allows operators to focus on interpreting results rather than grappling with data manipulation. ChatGrid produces its front-end visualizations through an LLM-powered query interface.
The visualization component includes five geospatial network layers that present the spatial patterns and distributions of generation, capacity, voltage, and power flow information of different power facilities throughout the country. These layers include a network layer, a generator layer, an animated flow layer, a county load layer, and a county voltage layer, all projected in 2.5D to reduce visual clutter.
“We decided to simplify obtaining desired information by supporting natural language query on the visualization,” Jin said. “This allows users to pose questions about the power grid network and receive visualizations and text summaries as responses.”

ChatGrid is deployed on a simulated dataset output by the Exascale Grid Optimization (ExaGO) model co-developed by PNNL. The model requires a supercomputer to operate. It simulates the nation’s power grid in real time, and grid operators can analyze the effects of any disruption.
Jin said the first version of ChatGrid provides a novel way for grid operators to access the large-scale power grid dataset and extract information through conversational interactions. The next step of ChatGrid will be integrating advanced simulation and optimization tools to handle more complex analytics tasks, such as contingency scenarios.
The research team also designed ChatGrid to protect the security of the nation’s highly sensitive grid data by securing it in a local environment and not exposing it to LLMs or their training process. The data is stored in a spatial database, and the LLMs are prompted to generate structured query language (SQL) clauses to retrieve the necessary information for answering user questions.
Click here to read PNNL’s news release on ChatGrid.


